1.多线程
1.1线程与进程的关系
进程是资源分配的最小单位,线程是调度的最小单位。
线程是轻量级的进程,是比进程粒度更小的单位。线程本身不占用资源,和进程共享一个资源[0-3G]的用户空间。
线程没有进程安全。如果线程导致进程崩溃,其他线程都不能执行了。进程死掉并不会对另外一个进程造成影响。
线程的效率比进程高。
线程使用的是第三方库函数。
1.2线程的创建函数pthread_create
#include<pthread.h>
int pthread_create(pthread_t *thread, const pthread_attr_t *attr,
void *(*start_routine) (void *), void *arg);
功能:创建一个线程
参数:
@thread:线程号地址
@attr:线程属性,NULL
@start_routine:线程处理函数
@arg:向线程处理函数传递的参数
返回值:
成功:返回0
失败:返回错误码(*thread:线程号没有定义)
注:编译和链接使用 -pthread。
pthread_create代码如下(不传参):
#include<stdio.h>
#include<pthread.h>
#include<errno.h>
#define PRINT_ERR(msg) \
do \
{ \
printf("%s %s %d\n",__FILE__,__func__,__LINE__); \
perror(msg); \
return -1; \
} while (0)
void *task(void *arg){
printf("i am thread....\n");
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
pthread_t tid;
if((errno = pthread_create(&tid, NULL, task, NULL)) != 0){
PRINT_ERR("pthread create error");
};
printf("i am parent thread\n");
while (1); //线程的执行没有先后顺序,不加这句可能直接退出了。
return 0;
}
结果展示:

pthread_create代码如下(传参):
#include<stdio.h>
#include<pthread.h>
#include<errno.h>
#define PRINT_ERR(msg) \
do \
{ \
printf("%s %s %d\n",__FILE__,__func__,__LINE__); \
perror(msg); \
return -1; \
} while (0)
typedef struct{
char name[30];
int score;
}s_t;
void *task1(void *arg){
printf("i am task1....\n");
printf("ctid = %ld\n",*(pthread_t *)arg);
}
void *task2(void *arg){
s_t *t = (s_t *)arg;
printf("i am task2....\n");
printf("name = %s,socre = %d\n", t->name, t->score);
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
pthread_t tid1, tid2;
s_t s = {
.name = "ning",
.score = 100,
};
//传递整数
if((errno = pthread_create(&tid1, NULL, task1, (void*)&tid1)) != 0){
PRINT_ERR("pthread create error");
};
//传递结构体
if((errno = pthread_create(&tid2, NULL, task2, (void*)&s)) != 0){
PRINT_ERR("pthread create error");
};
printf("ptid1 = %ld, ptid2 = %ld\n", tid1, tid2);
printf("i am parent thread\n");
while (1); //线程的执行没有先后顺序,不加这句可能直接退出了。
return 0;
}
结果展示:

1.2.1线程执行顺序
线程执行没有先后顺序,时间片轮询,上下文切换。
1.2.2线程内存空间问题
如果有一个全局变量,那么多个线程都可以使用这个全局变量,因为线程共享进程的资源。
#include<stdio.h>
#include<pthread.h>
#include<errno.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define PRINT_ERR(msg) \
do \
{ \
printf("%s %s %d\n",__FILE__,__func__,__LINE__); \
perror(msg); \
return -1; \
} while (0)
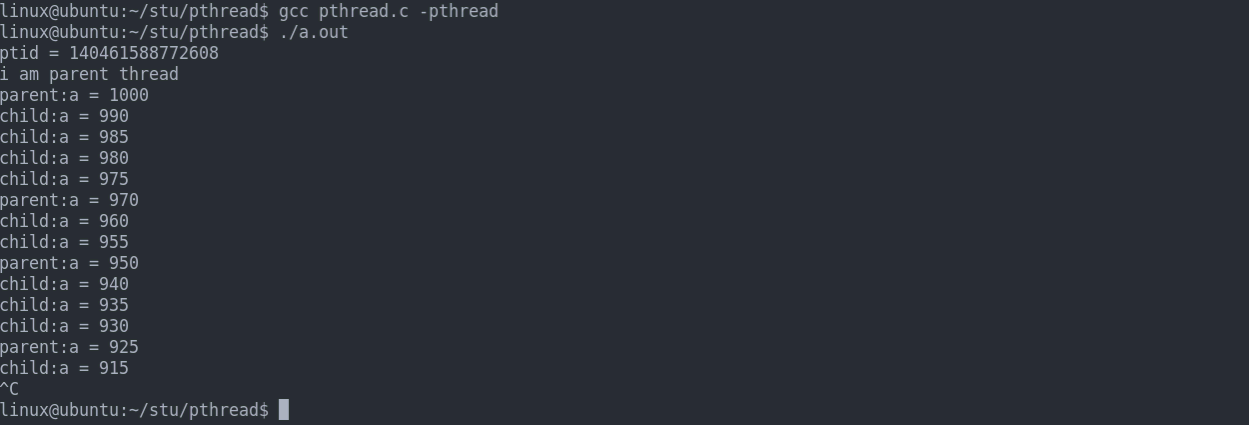
int a = 1000;
void *task(void *arg){
while (1){
printf("child:a = %d\n",a);
a -= 5;
sleep(1);
}
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
pthread_t tid;
if((errno = pthread_create(&tid, NULL, task, NULL)) != 0){
PRINT_ERR("pthread create error");
};
printf("ptid = %ld\n", tid);
printf("i am parent thread\n");
while (1){
printf("parent:a = %d\n",a);
a -= 10;
sleep(3);
}
return 0;
}
结果展示:
1.2.3综合练习使用多线程拷贝同一个文件
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#define PRINT_ERR(msg) \
do \
{ \
printf("%s %s %d\n",__FILE__,__func__,__LINE__); \
perror(msg); \
return -1; \
} while (0)
typedef struct {
const char * src;
const char * dest;
int start;
int len;
}file_t;
int get_file_len(const char *src, const char *dest)
{
int fd1, fd2, len;
if((fd1 = open(src, O_RDWR)) == -1){
PRINT_ERR("open error");
}
if((fd2 = open(dest, O_RDWR | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC, 0666)) == -1){
PRINT_ERR("open error");
}
len = lseek(fd1, 0, SEEK_END);// 返回文件的字节数
close(fd1);
close(fd2);
return len;
}
int copy_file(const char *src, const char *dest, int start, int len){
int sfd, dfd, ret, count = 0;
char buf[128] = {0};
if ((sfd = open(src, O_RDONLY)) == -1){
PRINT_ERR("open src error");
}
if ((dfd = open(dest, O_RDWR)) == -1){
PRINT_ERR("open src error");
}
lseek(sfd, start, SEEK_SET); //从头向后偏移
lseek(dfd, start, SEEK_SET);
while ((ret = read(sfd, buf, sizeof(buf))) != 0)
{
count += ret; //len
if(count > len) { //| |多count-len
write(dfd, buf, ret - (count - len)); //|————————|————|————|
//ret-(多)
break;
}
write(dfd, buf, ret);
}
close(sfd);
close(dfd);
return 0;
}
void *task(void *arg){
file_t *f = (file_t *)arg;
copy_file(f->src, f->dest, f->start, f->len);
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
pthread_t tid1, tid2;
int len;
// 1.检查参数
if (argc != 3) {
fprintf(stderr, "input error,try again\n");
fprintf(stderr, "./a.out srcfile destfile\n");
return -1;
}
// 2.获取源文件的长度并初始化目标文件
len = get_file_len(argv[1], argv[2]);
// 3.多线程拷贝同一个文件
file_t f[] = {
[0] = {
.src = argv[1],
.dest = argv[2],
.start = 0,
.len = len / 2,
},
[1] = {
.src = argv[1],
.dest = argv[2],
.start = len / 2,
.len = len - len / 2,
},
};
if ((errno = pthread_create(&tid1, NULL, task, (void *)&f[0])) != 0)
PRINT_ERR("pthread create error");
if ((errno = pthread_create(&tid2, NULL, task, (void *)&f[1])) != 0)
PRINT_ERR("pthread create error");
printf("tid = %ld,tid2 = %ld\n", tid1, tid2);
pthread_join(tid1,NULL);
pthread_join(tid2,NULL);
return 0;
}
结果展示:

1.3获取线程号的函数pthread_self
pthread_t pthread_self(void);
功能:获取当前线程的线程号
参数:
@无
返回值:
总是会成功,返回线程号。
pthread_self代码如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <errno.h>
#define PRINT_ERR(msg) \
do \
{ \
printf("%s %s %d\n",__FILE__,__func__,__LINE__); \
perror(msg); \
return -1; \
} while (0)
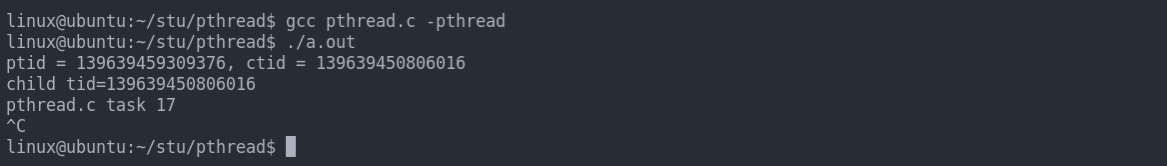
void *task(void *arg){
printf("child tid=%ld\n", pthread_self());
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
pthread_t tid;
if ((errno = pthread_create(&tid, NULL, task, NULL)) != 0) {
PRINT_ERR("pthread create error");
}
printf("ptid = %ld, ctid = %ld\n",pthread_self(), tid);
while (1);
return 0;
}
结果展示:

1.4线程退出函数pthread_exit
在线程中不能够使用exit/_exit退出一个线程,因为这两个函数是结束进程的函数。
void pthread_exit(void *retval);
功能:退出当前线程
参数:
@retval:退出的状态,与exit里面的值类似
返回值:
无
pthread_exit代码如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define PRINT_ERR(msg) \
do \
{ \
printf("%s %s %d\n",__FILE__,__func__,__LINE__); \
perror(msg); \
return -1; \
} while (0)
void *task(void *arg){
printf("child tid=%ld\n", pthread_self());
while(1){
printf("%s %s %d\n",__FILE__,__func__,__LINE__);
sleep(1);
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
pthread_t tid;
if ((errno = pthread_create(&tid, NULL, task, NULL)) != 0) {
PRINT_ERR("pthread create error");
}
printf("ptid = %ld, ctid = %ld\n",pthread_self(), tid);
while (1);
return 0;
}
结果展示:
1.5线程资源回收函数pthread_join
int pthread_join(pthread_t thread, void **retval);
功能:阻塞等待子线程的结束,如果子线程结束了,为它回收资源。(线程必须是结合态)
参数:
@thread:线程号
@retval:接收pthread_exit返回的值
返回值:
成功:返回0
失败:返回错误码
pthread_join代码如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define PRINT_ERR(msg) \
do \
{ \
printf("%s %s %d\n",__FILE__,__func__,__LINE__); \
perror(msg); \
return -1; \
} while (0)
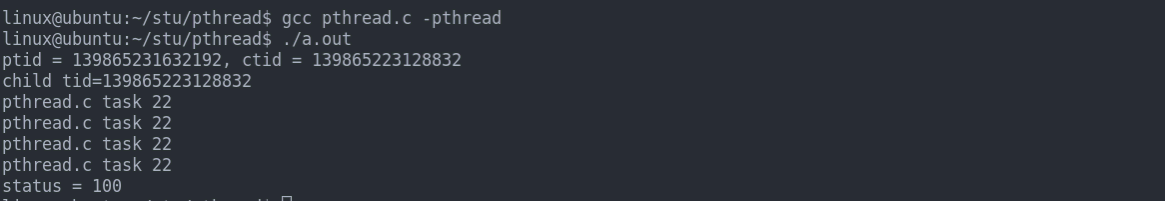
void *task(void *arg){
int i = 5;
printf("child tid=%ld\n", pthread_self());
//status变量不能在栈上,如果在栈空间,子线程执行结束后内存就释放掉了,
//在主线程中pthread_join的第二个参数就不能够拿到这个结果了。
//解决方法在status前加static,或者将status定义成全局变量或者使用malloc给status分配堆空间。
static int status = 100;
while(--i){
printf("%s %s %d\n",__FILE__,__func__,__LINE__);
sleep(1);
}
pthread_exit(&status);
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
pthread_t tid;
if ((errno = pthread_create(&tid, NULL, task, NULL)) != 0) {
PRINT_ERR("pthread create error");
}
printf("ptid = %ld, ctid = %ld\n",pthread_self(), tid);
int *status;
pthread_join(tid, (void **)&status);
printf("status = %d\n", *status);
return 0;
}
结果展示:
1.6线程分离态函数pthread_detach
线程的状态分别有结合态和分离态。
结合态的线程资源需要通过pthread_join来回收,分离态的线程资源自动回收。
int pthread_detach(pthread_t thread);
功能:将线程标记为分离态,分离态的线程资源自动被回收
参数:
@thread:线程号
返回值:
成功:返回0
失败:返回错误码
pthread_detach代码如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define PRINT_ERR(msg) \
do \
{ \
printf("%s %s %d\n",__FILE__,__func__,__LINE__); \
perror(msg); \
return -1; \
} while (0)
void *task(void *arg){
int i = 5;
printf("child tid=%ld\n", pthread_self());
static int status = 100;
pthread_detach(pthread_self());
while(--i){
printf("%s %s %d\n",__FILE__,__func__,__LINE__);
sleep(1);
}
pthread_exit(&status);
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
pthread_t tid;
if ((errno = pthread_create(&tid, NULL, task, NULL)) != 0) {
PRINT_ERR("pthread create error");
}
printf("ptid = %ld, ctid = %ld\n",pthread_self(), tid);
while(1);
return 0;
}
结果展示:

1.7线程发送取消信号函数pthread_cancel
int pthread_cancel(pthread_t thread);
功能:一个线程给另一个线程发送取消信号,收到信号的线程将自动停止
参数:
@thread:线程号
返回值:
成功:返回0
失败:返回错误码
注意:
int pthread_setcancelstate(int state, int *oldstate)
功能:设置线程是否可以被取消
参数:
@state:是否可以被取消的状态
PTHREAD_CANCEL_ENABLE:可被取消
PTHREAD_CANCEL_DISABLE: 不可被取消
@oldstate:原来的状态
返回值:
成功:返回0
失败:返回错误码
int pthread_setcanceltype(int type, int *oldtype);
功能:设置线程取消的类型
参数:
@type:类型
PTHREAD_CANCEL_DEFERRED:延时取消
PTHREAD_CANCEL_ASYNCHRONOUS: 立即取消
@oldstate:原来的状态
返回值:
成功:返回0
失败:返回错误码
pthread_cancel代码如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define PRINT_ERR(msg) \
do \
{ \
printf("%s %s %d\n",__FILE__,__func__,__LINE__); \
perror(msg); \
return -1; \
} while (0)
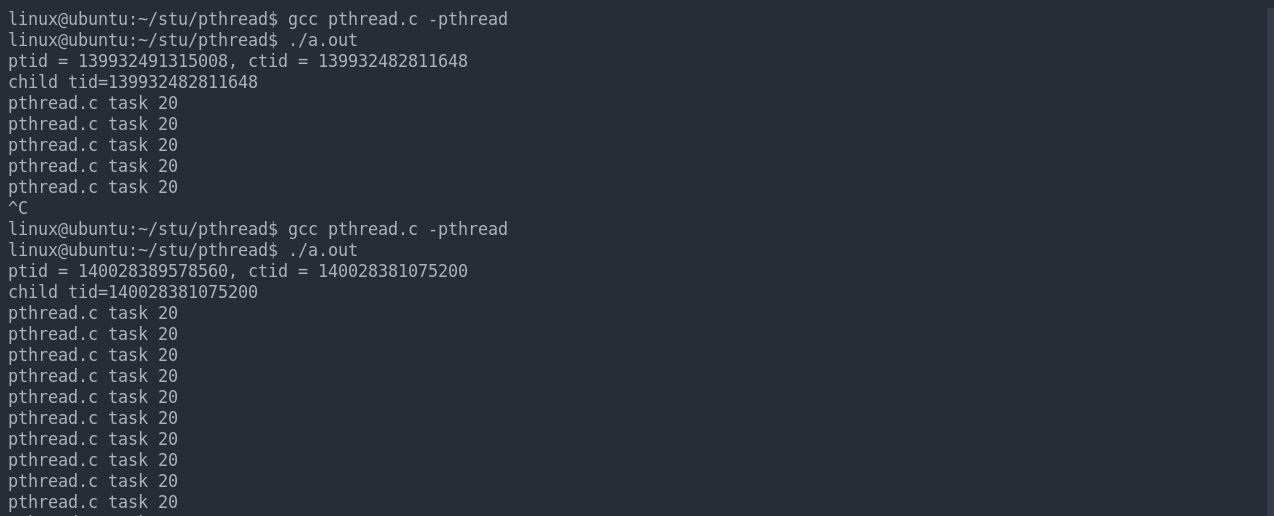
void *task(void *arg){
printf("child tid=%ld\n", pthread_self());
pthread_setcancelstate(PTHREAD_CANCEL_DISABLE, NULL);
//pthread_setcanceltype(PTHREAD_CANCEL_ASYNCHRONOUS, NULL);
while(1){
printf("%s %s %d\n",__FILE__,__func__,__LINE__);
sleep(1);
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
pthread_t tid;
if ((errno = pthread_create(&tid, NULL, task, NULL)) != 0) {
PRINT_ERR("pthread create error");
}
printf("ptid = %ld, ctid = %ld\n",pthread_self(), tid);
sleep(5);
pthread_cancel(tid);
while(1);
return 0;
}
结果展示:
2.线程的互斥机制
2.1线程互斥锁API
线程互斥机制实现的时候是资源争抢的过程,当一个线程获取到资源后,另一个线程就获取不到资源(休眠等)。
1.定义线程互斥锁变量
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
2.初始化线程的互斥锁
静态初始化:
pthread_mutex_t mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
动态初始化:
int pthread_mutex_init(pthread_mutex_t *mutex, const pthread_mutexattr_t *attr)
功能:初始化线程互斥锁
参数:
@mutex:被初始化的锁
@attr:缺省属性,一般填NULL
返回值:
成功:返回0
失败:返回错误码
3.上锁
int pthread_mutex_lock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex);
功能:上锁,如果锁之前没有被获取则获取锁成功,如果锁之前被获取则堵塞等待锁的资源
参数:
@mutex:互斥锁的变量地址
返回值:
成功:返回0
失败:返回错误码
int pthread_mutex_trylock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex);
功能:尝试上锁,如果锁之前没有被获取则获取锁成功,如果锁之前被获取则这个函数立即返回,表示获取锁失败
参数:
@mutex:互斥锁的变量地址
返回值:
成功:返回0
失败:返回错误码
4.解锁
int pthread_mutex_unlock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex);
功能:解锁
参数:
@mutex:互斥锁的变量地址
返回值:
成功:返回0
失败:返回错误码
5.销毁锁
int pthread_mutex_destory(pthread_mutex_t *mutex)
功能:销毁互斥锁
参数:
@mutex:互斥锁的变量地址
返回值:
成功:返回0
失败:返回错误码
代码示例如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define PRINT_ERR(msg) \
do \
{ \
printf("%s %s %d\n",__FILE__,__func__,__LINE__); \
perror(msg); \
return -1; \
} while (0)
int money=1000;
//定义互斥锁
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
void *task1(void *arg){
while(1){
//上锁
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
money -= 50;
if(money >= 0){
printf("张三取50块钱成功了,money=%d\n", money);
} else {
printf("张三取钱失败了\n");
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
sleep(1);
//解锁
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
}
}
void *task2(void *arg){
while(1){
//上锁
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
money -= 100;
if(money >= 0){
printf("李四取100块钱成功了,money=%d\n", money);
} else {
printf("李四取钱失败了\n");
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
sleep(1);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
}
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
pthread_t tid1, tid2;
//初始化互斥锁
pthread_mutex_init(&mutex, NULL);
if ((errno = pthread_create(&tid1, NULL, task1, NULL)) != 0) {
PRINT_ERR("pthread create error");
}
if ((errno = pthread_create(&tid2, NULL, task2, NULL)) != 0) {
PRINT_ERR("pthread create error");
}
pthread_join(tid1, NULL);
pthread_join(tid2, NULL);
pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex);
return 0;
}
结果展示:

注:上述程序执行的效果:可以能张三线程执行了很多次,然后李四线程才执行。还有可能李四线程执行了很多次,然后张三线程才执行。但是一定不会出现竞态的现象了。如果上述的程序不使用互斥锁,有可能在某次执行的时候张三和李四的线程在同一个数字的基础上往下同时减的现象。
3.线程的同步机制
线程同步机制是指:线程的执行顺序已经提前规划好了,常用的线程同步机制有无名信号量和条件变量。
线程的同步机制常用于来解决生产者和消费者模型。
3.1无名信号量
#include <semaphore.h>
1.定义无名信号量
sem_t sem;
2.初始化无名信号量
int sem_init(sem_t *sem, int pshared, unsigned int value);
功能:初始化无名信号量
参数:
@sem:无名信号量的变量地址
@pshared:
0:两个线程同步
1:两个进程同步
@value:信号量的初始值
如果value非0,表示线程可以获取信号量
如果value为0,表示线程获取不到信号量,将阻塞
返回值:
成功:返回0
失败:返回-1置位错误码
3.获取无名信号量(P操作)
int sem_wait(sem_t *sem);
功能:获取无名信号量(如果获取不到就阻塞等待)value-1
参数:
@sem:无名信号量的变量地址
返回值:
成功:返回0
失败:如果失败信号量的值没有改变,返回-1置位错误码
4.释放无名信号量(V操作)
int sem_post(sem_t *sem);
功能:释放无名信号量 value+1
参数:
@sem:无名信号量的变量地址
返回值:
成功:返回0
失败:如果失败信号量的值没有改变,返回-1置位错误码
5.销毁无名信号量
int sem_destory(sem_t *sem);
功能:销毁无名信号量
参数:
@sem:无名信号量的变量地址
返回值:
成功:返回0
失败:返回-1置位错误码
代码示例如下(使用sleep):
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
#define PRINT_ERR(msg) \
do \
{ \
printf("%s %s %d\n",__FILE__,__func__,__LINE__); \
perror(msg); \
return -1; \
} while (0)
//定义无名信号量
sem_t sem;
//生产者线程
void *task1(void *arg){
while(1){
sleep(1);
printf("我生产了一个芯片\n");
//V操作
sem_post(&sem);
}
}
//消费者线程
void *task2(void *arg){
while(1){
//P操作
sem_wait(&sem);
printf("我购买了一个芯片\n");
}
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
pthread_t tid1, tid2;
//初始化无名信号量
sem_init(&sem, 0, 0);
if ((errno = pthread_create(&tid1, NULL, task1, NULL)) != 0) {
PRINT_ERR("pthread create error");
}
if ((errno = pthread_create(&tid2, NULL, task2, NULL)) != 0) {
PRINT_ERR("pthread create error");
}
pthread_join(tid1, NULL);
pthread_join(tid2, NULL);
sem_destroy(&sem);
return 0;
}
结果展示:
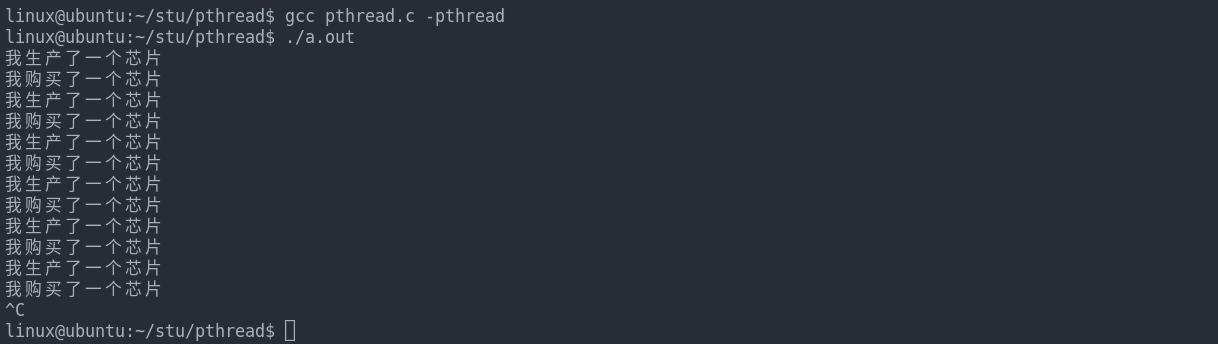
代码示例如下(不使用sleep):
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
#define PRINT_ERR(msg) \
do \
{ \
printf("%s %s %d\n",__FILE__,__func__,__LINE__); \
perror(msg); \
return -1; \
} while (0)
//定义无名信号量
sem_t sem1, sem2;
//生产者线程
void *task1(void *arg){
while(1){
//P操作
sem_wait(&sem1);
printf("我生产了一个芯片\n");
//V操作
sem_post(&sem2);
}
}
//消费者线程
void *task2(void *arg){
while(1){
//P操作
sem_wait(&sem2);
printf("我购买了一个芯片\n");
//V操作
sem_post(&sem1);
}
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
pthread_t tid1, tid2;
//初始化无名信号量
sem_init(&sem1, 0, 1);
sem_init(&sem2, 0, 0);
if ((errno = pthread_create(&tid1, NULL, task1, NULL)) != 0) {
PRINT_ERR("pthread create error");
}
if ((errno = pthread_create(&tid2, NULL, task2, NULL)) != 0) {
PRINT_ERR("pthread create error");
}
pthread_join(tid1, NULL);
pthread_join(tid2, NULL);
sem_destroy(&sem1);
sem_destroy(&sem2);
return 0;
}
结果展示:

代码示例:三个线程,其中线程1打印A,其中线程2打印B,其中线程3打印B.实现效果ABCABCABC…
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
#define PRINT_ERR(msg) \
do \
{ \
printf("%s %s %d\n",__FILE__,__func__,__LINE__); \
perror(msg); \
return -1; \
} while (0)
//定义无名信号量
sem_t sem1, sem2, sem3;
//生产者线程
void *task1(void *arg){
while(1){
//P操作
sem_wait(&sem1);
printf("A");
//V操作
sem_post(&sem2);
}
}
//消费者线程
void *task2(void *arg){
while(1){
//P操作
sem_wait(&sem2);
printf("B");
//V操作
sem_post(&sem3);
}
}
void *task3(void *arg){
while(1){
//P操作
sem_wait(&sem3);
printf("C");
//V操作
sem_post(&sem1);
}
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
pthread_t tid1, tid2, tid3;
//初始化无名信号量
sem_init(&sem1, 0, 1);
sem_init(&sem2, 0, 0);
sem_init(&sem3, 0, 0);
if ((errno = pthread_create(&tid1, NULL, task1, NULL)) != 0) {
PRINT_ERR("pthread create error");
}
if ((errno = pthread_create(&tid2, NULL, task2, NULL)) != 0) {
PRINT_ERR("pthread create error");
}
if ((errno = pthread_create(&tid3, NULL, task3, NULL)) != 0) {
PRINT_ERR("pthread create error");
}
pthread_join(tid1, NULL);
pthread_join(tid2, NULL);
pthread_join(tid3, NULL);
sem_destroy(&sem1);
sem_destroy(&sem2);
sem_destroy(&sem3);
return 0;
}
结果展示:

3.2条件变量
1.定义条件变量
pthread_cond_t cond;
2.初始化条件变量
静态初始化:(栈上初始化)
pthread_cond_t cond = PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER;
动态初始化:(堆上初始化)
int pthread_cond_init(pthread_cond_t *cond, const pthread_condattr_t *attr);
功能:初始化条件变量
参数:
@cond:条件变量的变量地址
@attr:缺省属性,默认NULL
返回值:
成功:返回0
失败:返回错误码
3.获取条件变量
int pthread_cond_wait(pthread_cond_t *cond, pthread_mutex_t *mutex);
功能:获取条件变量
参数:
@cond:条件变量的变量地址
@mutex:互斥锁变量的变量地址
返回值:
成功:返回0
失败:返回错误码
*使用流程:与互斥锁配合使用
1.先获取互斥锁
2.调用pthread_cond_wait
2.1将当前线程放到队列中
2.2解锁
2.3在队列中休眠
2.4重新获取锁
2.5从队列中移除
3.执行代码
4.解锁
4.释放条件变量
int pthread_cond_signal(pthread_cond_t *cond);
功能:释放一个资源
参数:
@cond:条件变量的变量地址
返回值:
成功:返回0
失败:返回错误码
int pthread_cond_broadcast(pthread_cond_t *cond);
功能:释放所有的资源
参数:
@cond:条件变量的变量地址
返回值:
成功:返回0
失败:返回错误码
5.销毁条件变量
int pthread_cond_destory(pthread_cond_t *cond);
功能:销毁条件变量
参数:
@cond:条件变量的变量地址
返回值:
成功:返回0
失败:返回错误码
代码示例:(一个消费者线程)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define PRINT_ERR(msg) \
do \
{ \
printf("%s %s %d\n",__FILE__,__func__,__LINE__); \
perror(msg); \
return -1; \
} while (0)
//定义互斥锁
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
//定义条件变量
pthread_cond_t cond;
//生产者线程
void *task1(void *arg){
while(1){
printf("我生成了一个芯片\n");
//V操作
pthread_cond_signal(&cond);
sleep(3);
}
}
//消费者线程
void *task2(void *arg){
while(1){
//P操作
pthread_cond_wait(&cond, &mutex);
printf("我购买了一个芯片\n");
}
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
pthread_t tid1, tid2;
//初始化互斥锁
pthread_mutex_init(&mutex, NULL);
//初始化条件变量
pthread_cond_init(&cond, NULL);
if ((errno = pthread_create(&tid1, NULL, task1, NULL)) != 0) {
PRINT_ERR("pthread create error");
}
if ((errno = pthread_create(&tid2, NULL, task2, NULL)) != 0) {
PRINT_ERR("pthread create error");
}
pthread_join(tid1, NULL);
pthread_join(tid2, NULL);
pthread_cond_destroy(&cond);
pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex);
return 0;
}
结果展示:
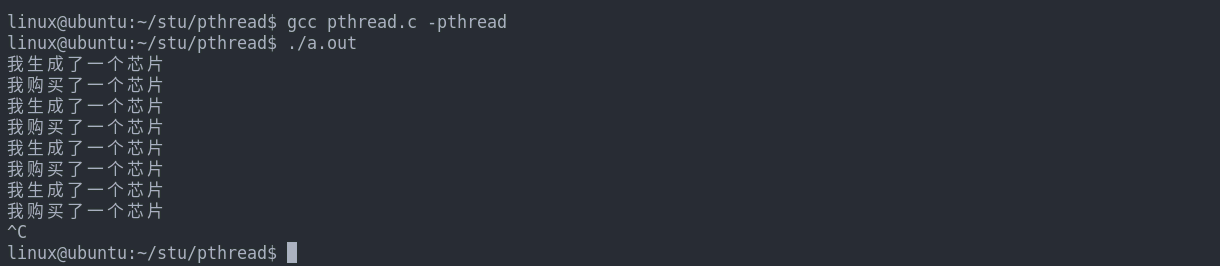
代码示例:(多个消费者线程)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define PRINT_ERR(msg) \
do \
{ \
printf("%s %s %d\n",__FILE__,__func__,__LINE__); \
perror(msg); \
return -1; \
} while (0)
//定义互斥锁
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
//定义条件变量
pthread_cond_t cond;
//生产者线程
void *task1(void *arg){
while(1){
printf("我生成了一个芯片\n");
//V操作
pthread_cond_signal(&cond);
//pthread_cond_broadcast(&cond);通知唤醒所有消费者线程
sleep(3);
}
}
//消费者线程
void *task2(void *arg){
while(1){
//P操作
//1.获取互斥锁
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
//2.获取条件变量
pthread_cond_wait(&cond, &mutex);
//3.执行代码
printf("tid=%ld,我购买了一个芯片\n", pthread_self());
//4.解锁
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
}
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
pthread_t tid1, tid2, tid3, tid4, tid5;
//初始化互斥锁
pthread_mutex_init(&mutex, NULL);
//初始化条件变量
pthread_cond_init(&cond, NULL);
if ((errno = pthread_create(&tid1, NULL, task1, NULL)) != 0) {
PRINT_ERR("pthread create error");
}
if ((errno = pthread_create(&tid2, NULL, task2, NULL)) != 0) {
PRINT_ERR("pthread create error");
}
if ((errno = pthread_create(&tid3, NULL, task2, NULL)) != 0) {
PRINT_ERR("pthread create error");
}
if ((errno = pthread_create(&tid4, NULL, task2, NULL)) != 0) {
PRINT_ERR("pthread create error");
}
if ((errno = pthread_create(&tid5, NULL, task2, NULL)) != 0) {
PRINT_ERR("pthread create error");
}
printf("tid2 =%ld,tid3 = %ld,tid4=%ld,tid5=%ld\n", tid2, tid3, tid4, tid5);
pthread_join(tid1, NULL);
pthread_join(tid2, NULL);
pthread_join(tid3, NULL);
pthread_join(tid4, NULL);
pthread_join(tid5, NULL);
pthread_cond_destroy(&cond);
pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex);
return 0;
}
结果展示:
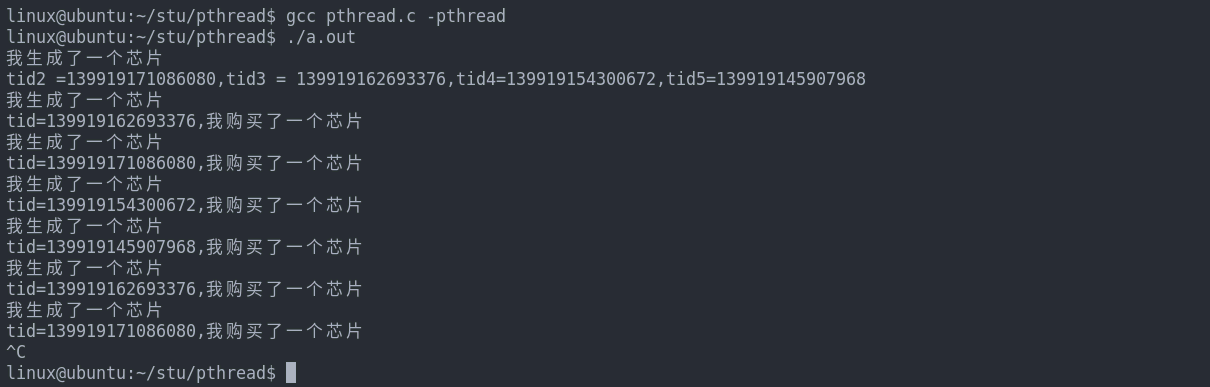
代码示例:使用条件变量实现两个线程的同步(不使用sleep)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define PRINT_ERR(msg) \
do \
{ \
printf("%s %s %d\n",__FILE__,__func__,__LINE__); \
perror(msg); \
return -1; \
} while (0)
//定义互斥锁
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
//定义条件变量
pthread_cond_t cond;
//定义标志位
int flag = 0;
//生产者线程
void *task1(void *arg){
while(1){
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
if(flag==1){
pthread_cond_wait(&cond,&mutex);
}
printf("我生成了一个芯片\n");
flag=1;
pthread_cond_signal(&cond);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
}
}
//消费者线程
void *task2(void *arg){
while(1){
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
if(flag==0){
pthread_cond_wait(&cond,&mutex);
}
printf("我购买了一个芯片\n");
flag=0;
pthread_cond_signal(&cond);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
}
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
pthread_t tid1, tid2, tid3, tid4, tid5;
//初始化互斥锁
pthread_mutex_init(&mutex, NULL);
//初始化条件变量
pthread_cond_init(&cond, NULL);
if ((errno = pthread_create(&tid1, NULL, task1, NULL)) != 0) {
PRINT_ERR("pthread create error");
}
if ((errno = pthread_create(&tid2, NULL, task2, NULL)) != 0) {
PRINT_ERR("pthread create error");
}
pthread_join(tid1, NULL);
pthread_join(tid2, NULL);
pthread_cond_destroy(&cond);
pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex);
return 0;
}
结果展示:

3.3线程同步总结
无名信号量适合在线程数较少时进行使用实现线程同步,而条件变量适合在大量线程实现线程同步。
例如条件变量的使用场景如下:比如你要编写一个12306买票的服务器,当客户端访问服务器的时候,服务器会创建一个线程服务于这个用户。如果有多个用户同时想买票,此时服务需要在瞬间创建一堆线程,这个时间比较长,对用户的体验感不好。所以12306服务是在启动的时候都已经创建好一堆线程。调用pthread_cond_wait让这些线程休眠,当有客户端请求买票的时候,只需要唤醒这些休眠的线程即可,由于省去了创建线程的时候,所以这种方式的效率非常的高。